Do you want to identify which business model is best for a wholesale/retail business? You can identify a business model by evaluating successful business models that have already been tried and tested by others. A business model is best for a service business if it can lead to efficient operations. This allows a business to use proven models, thereby avoiding making mistakes made by peers in that industry.
Find below business models best suited for service businesses and examples of firms using those models:
1) Solution Provider
A company provides a full package of related products and services with the aim of meeting customer needs. The solution can include several products and services such as maintenance, installation and support from the customer services desk. At times the company will partner with other service providers for non-core services.
Example; Hilti

Hilti, construction products and services reseller, allows customers to pay a fixed monthly fee for using the tools. The package includes all services related to usage and maintenance of the tools. Furthermore, the company also offers tool park optimization support, fully servicing customer needs.
2) Eco & Green
Eco & Green model is used by a social enterprise that has a cause of ensuring that its activities are environmental friendly and sustainable while maximizing their profits. Customers will value the products and services of the company because there are positive ecological effects in addition to commercial goals.
Example; Starbucks

Starbucks purchases certified organic coffee and creates stores that save on energy used for air-conditioning by adjusting store temperature. They also use furniture made of 90% recycled material, making the stores ecological friendly and cost effective.
3) Self-service
These where a company lowers the prices of a product or services by letting customers perform part of the product or service delivery themselves. The lower prices result from the cost savings that the company replaces employees with self-service option and automated systems.
Example; Amazon Go

Amazon Go is a self-service system cashier-less system where customers shop and walk out of a store without needing to scan or interact with the cashier. This is made possible through a ceiling-mounted camera and shelf-weight sensors that track customers and items as they shop around the store.
A customer can’t enter without the Amazon Go app on your phone and the scanning of your unique code. As a customer shops in the store, Amazon’s AI tracks the picked items and adds them to their virtual cart and charges them when they leave.
4) No-frills
This is a business model where products and services have a minimum set of features. This enables the prices to be kept as low as possible.
Example; Aldi

Aldi is a supermarket that uses the no frills model by having stores that have a simple undecorated design. The product range is limited; products are left in “cardboard boxes and pallets” along the aisles.
5) Cross-selling
Cross-selling involves selling a different/new product to an existing customer base. It enables a company to grow its sales without having to incur the cost of acquiring new customers, which can also be time-consuming.
Example; Coccinelle
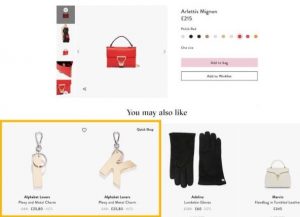
Coccinelle, an online store for premium bags and accessories for women, recommends other products that a customer may want when a customer purchases an item. A good percentage of its sales are as a result of cross-selling.
6) Barter
Products or services are traded for other products or services without money exchanged. This is a unique business model that has existed before money started being used as a form of exchange and should be considered when deciding which business model is best for a wholesale/retail business.
Example; Noppes

Noppes, Amsterdam-based local barter system, enables its users to trade products and services with each other such as food, transportation, computer services without the exchange of money.
7) E-Commerce only
With this model, products and services are sold online only without having a physical store. This enables a company to sell to its customer globally cost effectively 24/7.
Example; Alibaba

Alibaba, the world’s biggest online e-commerce company, uses this model. It has created different online versions of online auction eBay (Taobao), online retailer Amazon (Tmall), payment service Paypal (Alipay) and discount website Groupon (Juhuasuan).
8) Reselling
A company distributes products and services from another company; a manufacturer. The distributing company provides advice in addition to selling the product.
Example; Etsy

Etsy is a global online reseller that does not incur high overhead expenses of retail outlets. They focus on promoting products from creative entrepreneurs and help them scale their business.
9) Shop-in-shop
The shop-in-shop is a store in another store. This is a model where a store with a large area subdivides and sublets the extra space to other small enterprises generating additional revenue. The wide variety of products and services resulting from the arrangement also leads to increased customer traffic.
Example; Bloomingdale’s

Bloomingdale is a fashion and luxury store that has rented part of its store to Ralph Lauren, Calvin Klein, DKNY and Kenneth Cole.
10) Omnichannel
The model integrates online and physical channels enabling the customers to have a seamless, consistent shopping experience as they can easily switch channels.
Example; Carrefour

Carrefour, a Belgian supermarket chain, launched “Connected Kitchen” that enables customers to add items to their shopping basket using a self-scanner. Customers can add items to their shopping basket using voice recognition or by scanning the barcode. Before making a purchase, the customers can review the shopping list and choose to pick the products themselves or home delivery.
11) White label
This is where a company outsources its manufacturing function then sells the products under its brand. This can be a good model when deciding which Business Model is Best for A Wholesale/Retail Business. This arrangement is best for both the manufacturing business and the “white label” company.
Example; Costco
Costco is one of the largest resellers in the world though it does not bottle its own wine or own vineyards. Vineyards offer private label wines which Costco resells under its own label.
12) Revenue-sharing
In this business model, companies come together to make a product or provide a service, then share the revenues and risks. The revenue share is based on the contribution of specific partners or the costs/risks incurred.
Example; Groupon
Groupon, an online shopping discount e-commerce platform, promotes deals from (local) businesses and only allows a deal to go through when enough customers take it up. The company takes 50% of the resulting revenue from the sale.
13) Auction
A model in which a product or service is sold to the highest bidder. Customers that are willing to pay the highest price are selected through an auction. Auctions are mostly held online.
Example; Ebay
Ebay, an e-commerce platform, has auction services that allow sellers to sell their products on auction.
14) Bundling
A company sells multiple products together often at a discount instead of selling them separately. Even though bundling encourages customers to buy more, they may not be willing to pay more for additional bundled items and will be dissatisfied if a bundled item is taken away.
Example; Shopify
Shopify, an online e-commerce store, is known for bundling various products together to promote sales for its large number of businesses.
15) Business alliance
This is a model that involves several organizations coming together to achieve a common business goal. The collaboration may be to develop new products or services or cost reductions.
Example; Barnes & Noble Café

Barnes & Noble, an online bookstore, collaborated with Starbucks to create the Barnes & Noble Café after realizing that educated middle-class customers who visited Starbucks to drink latte were the same customers who bought their books. The alliance resulted in more sales for Barnes & Noble and Starbucks.
16) Franchising
This model involves the franchise, owner of a process, knowledge or trademark, giving the franchisee the licence to sell a product or service under the franchisers name. The franchiser in return receives a fixed fee and a percentage of the revenues generated.
Example; McDonald’s

McDonald’s a global franchising brand that has more than 80% of its restaurants owned and operated by franchisees. Franchisees pay an initial capital in cash and thereafter pay a percentage of the sales revenues.
17) Renting
A company receives income for temporary use of a product, service or property by another third party.
Example; Storefront
Storefront, the world’s largest marketplace for short-term retail spaces, provides rental spaces for supermarkets, cafes etc.
Conclusion
In conclusion, when deciding which business model is best for a wholesale/retail business it is important to consider all the business models mentioned in this article. When a business model matches the needs of the business, it results in efficient delivery of your product or service leading to increased customer loyalty and business growth.

