Do you want to identify which business model is best for a service business? One way is to review the business models being used by other players in your industry. Find below business models best suited for service businesses and examples of firms using those models:
1) Experience selling
The model involves a company giving their customers an experience by creating ambience around the product offering. The aim is to not just sell but create a customer emotional engagement with the product. This is achieved through creating a memorable event that increases the perceived value and enables the product to be sold at a premium.
Example; Disney World

Disney creates a magical and personalized experience for its customers by having thoughtful details around the park, ambient music, thrills of rides and staged entertainment. Clients pay to enjoy the memorable experience with an amazing 70% return rate of first-time guests.
2) Anything as a Service
Anything as a Service; products, tools and technologies are offered as services online. The users only pay for what they have consumed instead of purchasing the product.
Example; Philips

Philips, provider of innovative LED lighting solutions, through its Lighting-as-a-Service offering allows customers to pay for the energy used to light the lamps while still owning all the fixtures and lamps. The model serves customers well because the lamps are significantly expensive and thus become cost effective for the clients with this arrangement.
3) Platform
This is where a company uses a platform to aggregate information on goods or services providers then connect them to clients. The company offers the products or services under its own name, standardizing the quality of service and price; is responsible for payments and disputes. The company earns from a percentage of each transaction and advertisements on the platform.
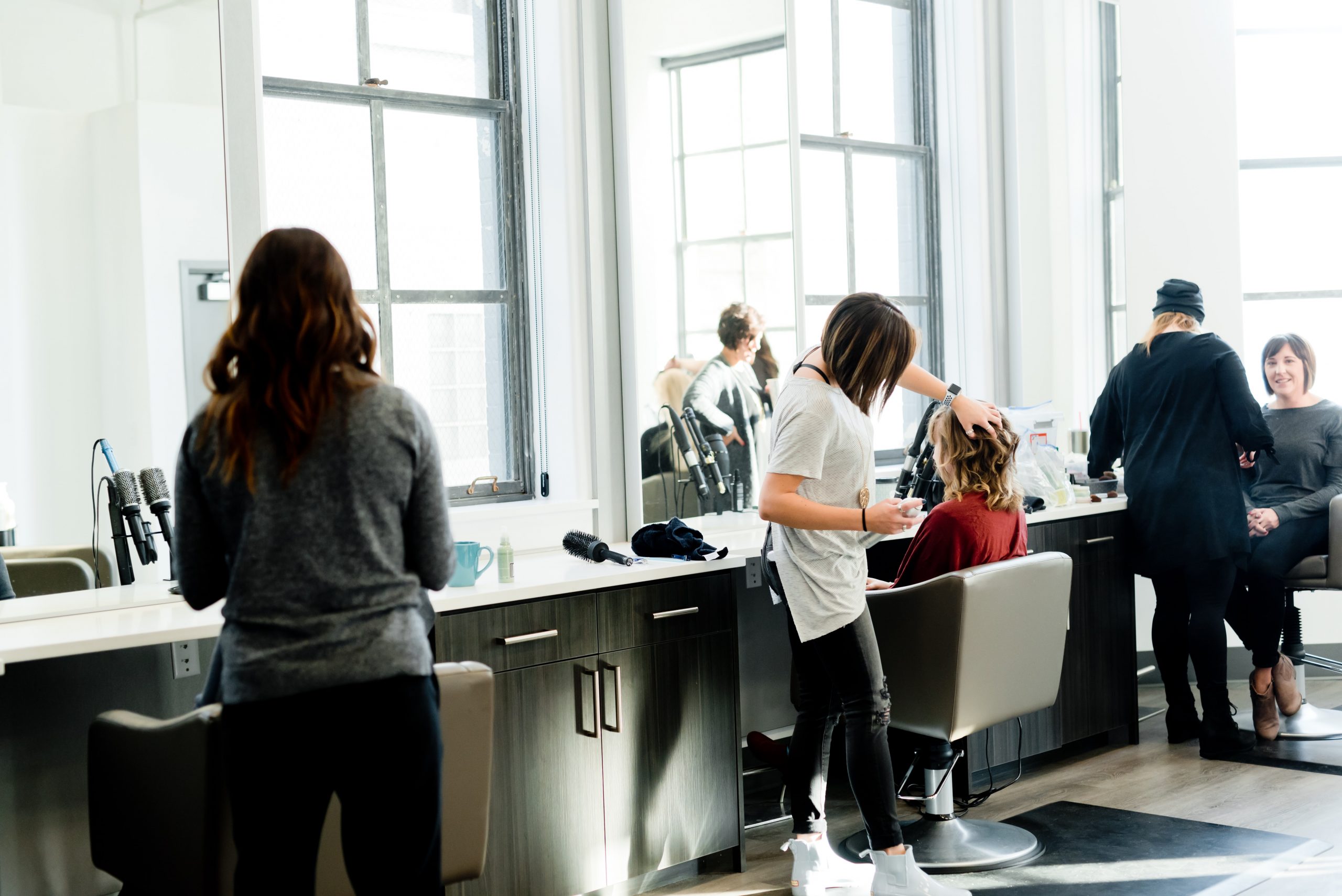
Example; Uber
Uber has a mobile app that connects passengers to taxi drivers. When the customer orders a ride through the app, it connects him/her to the nearest available driver by sharing their locations. Uber earns a fee from the fare the driver charges via the app.
4) Long tail
It is a business strategy of selling a large number of relatively low-demand products to many customers. When these products are sold together, they take a substantial part of the market share.
Example; Spotify
Spotify, a music streaming service, offers its users a vast catalogue of songs that they can choose from. Most of the songs are played by a few users, but the huge number of these songs attracts many users earning spotify a significant part of its revenues.
5) Sharing Economy
This model involves companies renting or sharing out under-utilized assets. Most of these assets are expensive and are not used all the time. This enables companies to have economies of scale.
Example; Peerby
The company has an online platform that enables users to share or borrow products with other users in the same neighbourhood. The items shared are products that the users need occasionally.
6) Cross-selling
Cross-selling involves selling a different/new product to an existing customer base. It enables a company to grow its sales without having to incur the cost of acquiring new customers, which can also be time-consuming. This makes it one of the important business models to adopt when researching on which business model is best for a service business.
Example; Amazon

When a customer purchases an item like an electronic, a recommended list of electronics is shown. Amazon has indicated that 35% of its sales are as a result of cross-selling.
7) Add-on
A basic product is offered to customers at an attractive price. The customer is then charged for each additional feature or service. Thus, customers are able to purchase customized products according to their needs and budget.
Example; Ryanair
The airline offers all customers low-cost basic affordable service. Customers pay additional fees for additional comfort and features.
8) Pay-per-use
Pay-per-use model is where a customer pays per service usage. The service usage is measured in units such as number of clicks, distance, time, calls or bytes, occasions.
Example; Zipcar

Zipcar, a car sharing service, allows clients to find and use available cars through an app. They reserve by the hour, by the day instead of using their own cars. When they have finished using the car, they pack it in the same location where they picked it up. The price is all-inclusive and covers gas, insurance, rental, maintenance and parking.
9) Auction
A model in which a product or service is sold to the highest bidder. Customers that are willing to pay the highest price are selected through an auction. Auctions are mostly held online.
When determining which business model is best for a service business the auction model is one of the model that an entrepreneur should consider as it leads to increased profit margins.
Example; Princess Holidays
Princess Holidays, a family-owned hotel-only holiday company, grew by offering holiday deals through the auction site Ebay. Initially, the transactions had small profit margins, but customers would return directly to its website each time they wanted to book a holiday.
10) Dynamic Pricing
Dynamic pricing is a model based on fluctuating prices due to customer demand or competitor pricing. It requires good monitoring mechanisms to track changes constantly.
Example; TUI

TUI, a travel agency, uses dynamic pricing based on customer demand. Tickets are put on sale when there is a risk a plane will take off half empty and vice versa.
11) Content curation
This model involves gathering information on a specific topic then helping customers to find and select relevant information that they need.
Example; Blendle

Blendle, an app and a website that provides access to articles from newspapers, publishers and magazines. Based on a user’s previous reading, the Blendle is able to gather and aggregate articles that suit a user’s preferences. Users search for articles and have a short window within which they can cancel an article purchase and get a refund.
12) Fractional ownership
Fractional ownership involves several unrelated parties jointly owning a high-value tangible asset. The parties share in the benefits of the asset such as income, priority access as well as `maintenance costs. The asset is not used full time by one party.
Example; NetJets

NetJets is an airline that offers customers a fractional ownership in an aircraft. Their costs include a one-time acquisition fee, a monthly management fee and a per-hour flight fee.
13) Renting
A company receives income for temporary use of a product, service or property by another third party.
Example; Rent the Runway

Run the Runway is a company that gives women access to high-fashion dresses and accessories on a rental basis. The customers choose a rent plan on the website and have the items delivered at their home by courier. This gives women the convenience of wearing expensive clothes for special occasions without buying or owning them.
14) Reverse auction
It is where the buyers create requests for services they need instead of sellers offering their services to buyers. These are mostly job board companies.
Example; Upwork

This is an online platform where clients post jobs and have the works chosen and done by expert freelancers with the right skillset. This gives the freelancers a great place to connect to clients, forge powerful relationships and grow their business.
Conclusion
Deciding on which business is best for a service business is important as it can determine the success or failure of a given venture. A good match between the business services and customer needs will lead to a win-win situation for everyone.

